Discover the most important types of bees, from honey bees and bumblebees to stingless and mason bees. Learn their roles in pollination, biodiversity, and why protecting them is vital for our planet.
Overview
Bees are essential pollinators, contributing to biodiversity and food production. With over 20,000 species, they vary in size, behavior, and ecological roles. Understanding different bee species helps in conservation efforts and sustainable beekeeping.
Bees are among the most crucial pollinators on Earth, supporting global biodiversity, food production, and healthy ecosystems. But not all bees are the same. With over 20,000 known species worldwide, bees vary widely in size, behavior, habitat, and ecological roles. Understanding the different types of bees not only enriches our appreciation of nature but also helps in conservation and sustainable agriculture.
In this guide, we explore the main types of bees, including their characteristics, roles in pollination, and significance to ecosystems.
1. Honeybees (Apis mellifera)

Characteristics:
- Social insects living in colonies.
- Produce honey and beeswax.
- Essential for commercial pollination.
Habitat & Behavior:
- Found worldwide in managed hives and wild colonies.
- Highly organized with a queen, workers, and drones.
- Communicate through the famous “waggle dance” to locate food sources.
Importance in Agriculture:
- Pollinate crops like almonds, apples, and blueberries.
- Contribute significantly to global food production.
2. Bumblebees (Bombus spp.)

Characteristics:
- Large, fuzzy bees with black and yellow markings.
- Excellent pollinators, especially for greenhouse crops.
Habitat & Behavior:
- Nest in underground burrows or grassy areas.
- Social but form smaller colonies than honeybees.
- Capable of “buzz pollination,” which helps release pollen from flowers like tomatoes.
Ecological Role:
- Pollinate wildflowers and crops that honeybees may not visit.
3. Carpenter Bees (Xylocopa spp.)
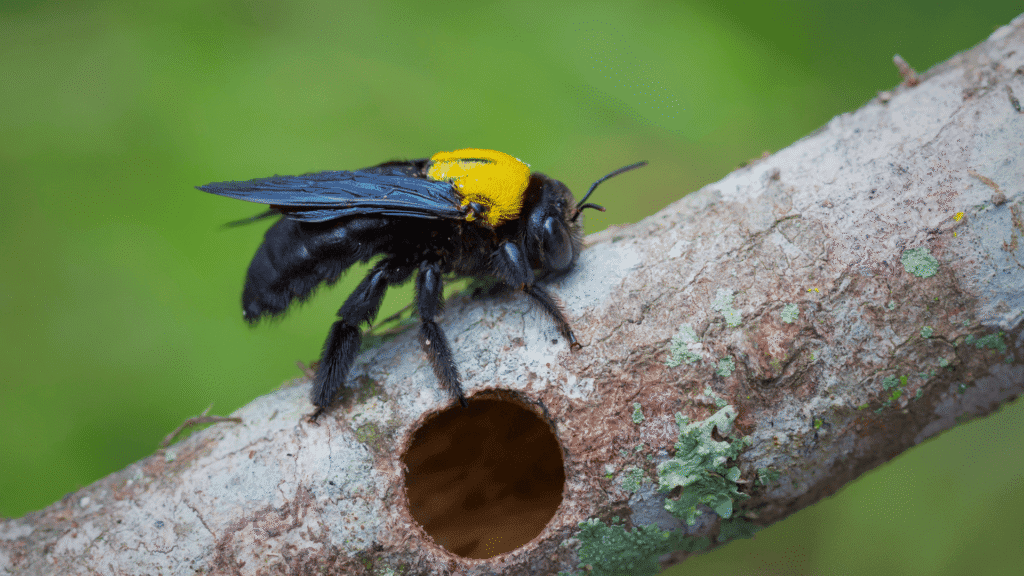

Characteristics:
- Large, solitary bees that burrow into wood.
- Often mistaken for bumblebees.
Habitat & Behavior:
- Prefer wooden structures for nesting.
- Beneficial pollinators but can damage wood.
- Males are territorial but do not sting.
Impact on Structures:
- Can weaken wooden buildings if infestations grow.
4. Mason Bees (Osmia spp.)

Characteristics:
- Small, metallic blue or green bees.
- Excellent pollinators for fruit trees.
Habitat & Behavior:
- Nest in hollow stems or artificial bee houses.
- Solitary but highly efficient pollinators.
- Do not produce honey but are vital for pollination.
Best Plants for Mason Bees:
- Apple, cherry, and pear trees.
5. Leafcutter Bees (Megachile spp.)

Characteristics:
- Medium-sized bees that cut leaves for nesting.
- Important pollinators for alfalfa and wildflowers.
Habitat & Behavior:
- Nest in hollow plant stems or wooden cavities.
- Solitary but contribute significantly to pollination.
- Use leaf fragments to construct nests.
Pollination Efficiency:
- More effective than honeybees for certain crops.
6. Sweat Bees (Halictidae family)

Characteristics:
- Small, often metallic green or black bees.
- Attracted to human sweat for moisture.
Habitat & Behavior:
- Nest in soil or rotting wood.
- Some species are social, while others are solitary.
- Important pollinators for wildflowers.
Unique Traits:
- Some species exhibit social behavior similar to honeybees.
7. Mining Bees (Andrenidae family)

Characteristics:
- Ground-nesting bees that dig tunnels.
- Important pollinators for wild plants.
Habitat & Behavior:
- Prefer sandy or loose soil for nesting.
- Solitary but contribute to ecosystem health.
- Active in early spring, making them crucial for early bloomers.
Best Plants for Mining Bees:
- Willow, maple, and fruit trees.
8. Stingless Bees (Meliponini tribe)
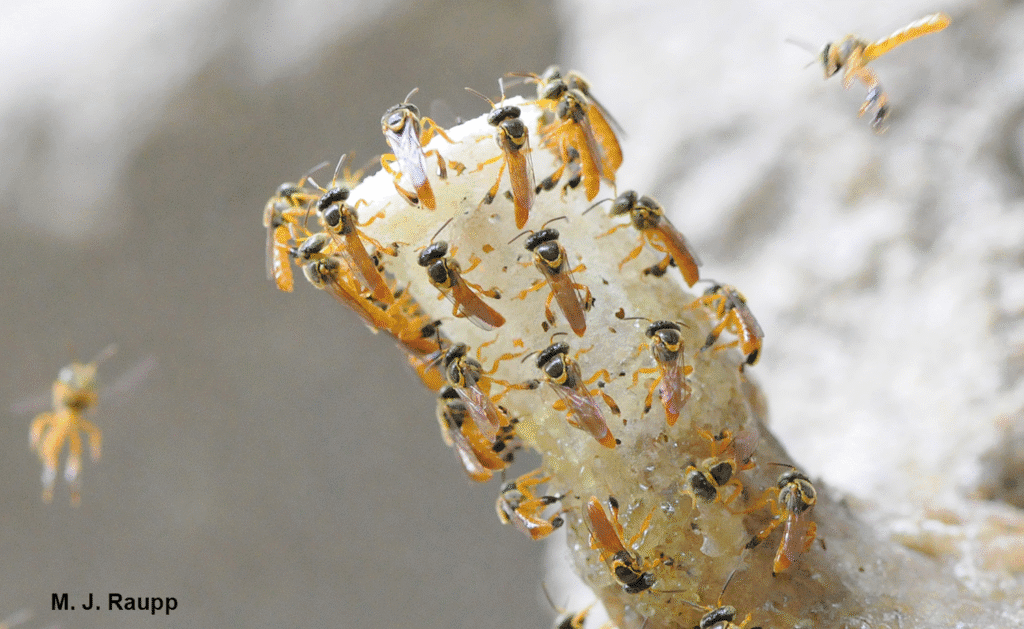
Characteristics:
- Small bees that do not sting.
- Produce medicinal honey.
Habitat & Behavior:
- Found in tropical regions.
- Live in colonies with complex social structures.
- Used in sustainable beekeeping practices.
Medicinal Honey Benefits:
- Antibacterial and antioxidant properties.
9. Blue Orchard Bees (Osmia lignaria)

Characteristics:
- Metallic blue bees specialized in orchard pollination.
- Highly efficient pollinators for fruit trees.
Habitat & Behavior:
- Nest in natural cavities or bee houses.
- Solitary but excellent pollinators for commercial orchards.
Best Plants for Blue Orchard Bees:
- Apples, cherries, and plums.
10. Squash Bees (Peponapis pruinosa)

Characteristics:
- Medium-sized bees specialized in pollinating squash plants.
- Active early in the morning before honeybees.
Habitat & Behavior:
- Nest in soil near squash plants.
- Solitary but essential for cucurbit pollination.
Best Plants for Squash Bees:
- Pumpkins, zucchini, and gourds.
FAQs
- What are the most important types of bees on Earth?
The most important types include honey bees, bumblebees, stingless bees, carpenter bees, mason bees, leafcutter bees, mining bees, and sweat bees. Each plays a unique role in ecosystems and agriculture. - Why are honey bees so important?
Honey bees are vital for crop pollination worldwide, supporting food production for humans and livestock. They also produce honey, wax, and propolis. - How do bumblebees differ from honey bees?
Bumblebees live in smaller colonies and are better suited for cooler climates. They are capable of buzz pollination, a technique honey bees cannot perform. - What makes stingless bees unique?
Stingless bees, found mainly in tropical regions, cannot sting but defend with bites and resin. They produce a special honey known for its medicinal properties. - Are carpenter bees harmful to humans?
Carpenter bees rarely sting and are not aggressive. While they bore into wood, they are also valuable pollinators of certain crops and plants. - Why are mason bees considered super pollinators?
Mason bees are highly efficient, with just a few hundred able to pollinate fruit orchards more effectively than thousands of honey bees. - What role do leafcutter bees play in agriculture?
Leafcutter bees are important pollinators for alfalfa, a crop essential for feeding livestock, and they also pollinate many wildflowers. - Where do mining bees live?
Mining bees nest underground, creating tunnels in sandy or loose soil. They are among the earliest bees to emerge in spring. - Why are sweat bees attracted to humans?
Sweat bees are drawn to the salt in human sweat, which they need for survival. They are generally harmless pollinators. - Do all bees produce honey?
No, only honey bees and some stingless bees produce honey in significant quantities. Most other bees focus solely on pollination. - How many species of bees exist worldwide?
There are more than 20,000 known species of bees, ranging from solitary to highly social types. - Why are solitary bees important if they don’t live in colonies?
Solitary bees like mason and leafcutter bees are highly efficient pollinators, often outperforming colony-based bees in specific crops. - What is buzz pollination and which bees can do it?
Buzz pollination is when a bee vibrates its body to release pollen from flowers. Bumblebees are the best-known buzz pollinators. - Which type of bee is best for fruit orchards?
Mason bees are excellent for fruit orchards due to their early-season activity and efficient pollination methods. - How are bees threatened today?
Major threats include pesticides, habitat loss, diseases, parasites like the Varroa mite, and climate change. - Are stingless bees good for farming?
Yes, stingless bees are increasingly used in tropical agriculture to pollinate crops such as coffee, mango, and guava. - Can carpenter bees replace honey bees?
No, while they are good pollinators, carpenter bees cannot match the large-scale agricultural pollination provided by honey bees. - How do bees support biodiversity?
Bees pollinate wildflowers, which support ecosystems by feeding other insects, birds, and animals, maintaining a balanced environment. - What can humans do to protect bees?
People can plant pollinator-friendly gardens, avoid pesticides, support sustainable farming, and protect natural habitats. - Why should we care about lesser-known bees like sweat bees or mining bees?
Even small and less famous species play crucial roles in pollination and ecosystem stability. Every bee contributes to biodiversity.
Would you like me to also craft a meta title and meta description (SEO-friendly) for this article to help it rank higher on Goog
Conclusion
Bees are not just honey producers; they are architects of ecosystems, guardians of biodiversity, and vital allies in agriculture. From honey bees to mason bees, each type plays a crucial role in ensuring the survival of plants, animals, and humans alike. Protecting them requires reducing pesticide use, conserving habitats, and promoting sustainable farming practices. By understanding their importance and diversity, we can better appreciate these tiny creatures that hold the key to life on Earth.
We pay $10 for a google review and We are looking for partnerships with other businesses for Google Review Exchange. Please contact us for more information!
Business Name: Sparkly Maid NYC Cleaning Services
Address: 447 Broadway 2nd floor #523, New York, NY 10013, United States
Phone Number: +1 646-585-3515
Website: https://sparklymaidnyc.com
I dont understand this kindly…
I pay a quick visit every day a few sites and
blogs to read content, except this blog gives feature based posts.
It’s remarkable in favor of me to have a site, which is
good for my know-how. thanks admin
You can mail me..vinysang6@mail.com…more guidelines..Thank you
My brother suggested I might like this website.
He was totally right. This post actually made my day.
You can not imagine just how much time I had spent for this information! Thanks!
Feel much appreciated Paito
Hi there! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be okay.
I’m undoubtedly enjoying your blog and look forward to new
posts.
I’ve been surfing online more than three hours today, yet
I never found any interesting article like yours. It’s pretty worth enough for me.
In my opinion, if all website owners and bloggers made good content
as you did, the web will be much more useful than ever before.
Thank you so much for your favourable response
For latest information you have to pay a quick visit world wide web and
on web I found this site as a finest site for newest updates.
Thank you so much my brother..Feel much appreciated
Hey would you mind stating which blog platform you’re using?
I’m planning to start my own blog soon but I’m having a difficult
time choosing between BlogEngine/Wordpress/B2evolution and Drupal.
The reason I ask is because your design and style seems different then most blogs and I’m looking for something
completely unique. P.S Sorry for getting off-topic but I had to
ask!
Thanks so much …feel much appreciated
Superb blog! Do you have any hints for aspiring writers?
I’m planning to start my own site soon but I’m a little lost on everything.
Would you recommend starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many options out there that I’m completely overwhelmed ..
Any tips? Thanks a lot!
You have to pay hosting company.Thanks
It’s very easy to find out any matter on web
as compared to books, as I found this paragraph at this web
site.
feel much welcomed once again
Hello to every one, it’s truly a pleasant for me to pay a visit this website,
it consists of useful Information.
thanks….feel much welcomed once again
Hi! Someone in my Facebook group shared this website with us so I came to give it a look.
I’m definitely enjoying the information. I’m book-marking and will be tweeting this to
my followers! Terrific blog and wonderful design.
Thank you so much…be blessed sir
good work. Continue updating the content….we are sharing it here